.webp)
The three most common email phishing techniques
Spoofing attacks have become increasingly prevalent these days, posing a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. Understanding these attacks and equipping ourselves with effective defense strategies is crucial in safeguarding our sensitive information and maintaining a secure online presence. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of spoofing techniques, learn how to detect and prevent email spoofing, identify cloned websites, and decode manual smart attacks. By the end of this article, you will have the knowledge and tools necessary to defend against spoofing attacks and mitigate the risks they pose.
1. Understanding Spoofing Attacks
Email spoofing is when a cybercriminal sends out a mass email to an extensive list of email addresses pretending to be from another sender. An excellent example of this which we see regularly is emails that have been designed to appear to come from well-known technology companies.These include:
- Microsoft Office 365
- Apple ID Login
- Amazon
- Adobe
Here is a perfect example of a spoofed email from what appears to be Office 365:
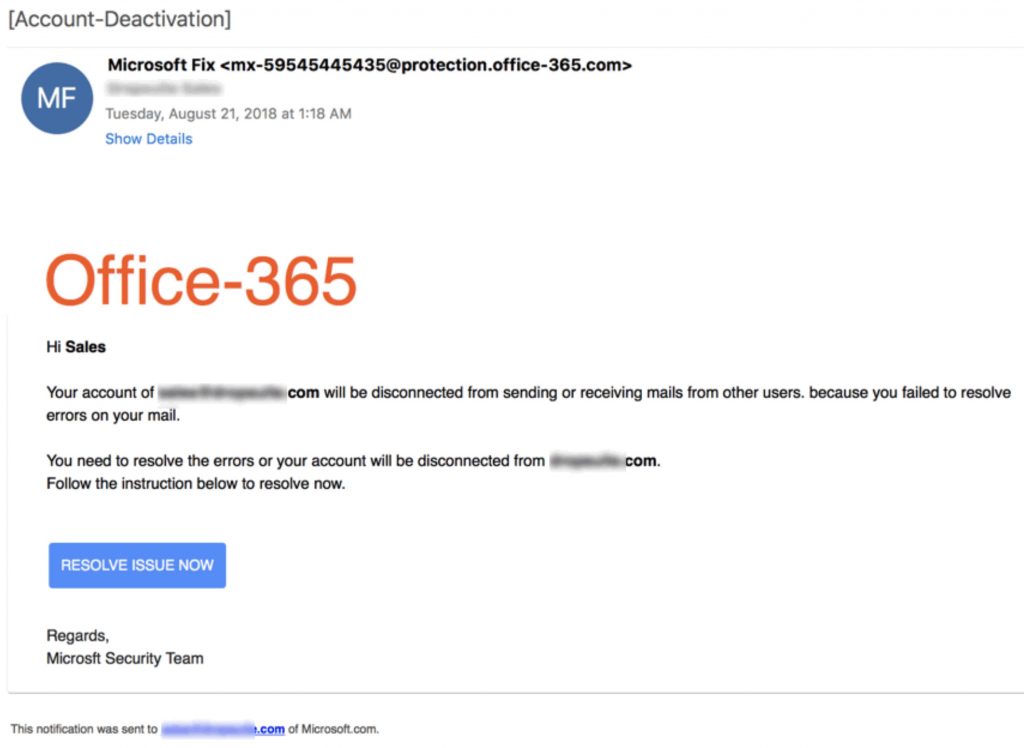
The only way to know that this email is legitimate or not is to look closely at the sender’s email address.In the example above the sender is office-365.com, which is not a domain owned by Microsoft.That’s the first error.The second is the “resolve issue now” button. Hovering over this link will reveal the URL to which the link goes. It is essential to check all links manually before you click.
2. Cloned Website
A cloned website is usually the second part of a spoofed email. When you click on a malicious URL in an email, it will take you to a page that looks like a genuine login screen for an online service you may use.These cloned websites are easily created by cyber criminals and can be replicated to many website domains.

Again, the only real way to know if it is an official website or not is by checking the URL in the address bar.If you are in doubt, then it’s worth raising a support ticket with your IT provider or department.Many online services now attempt to block malicious websites once reported.Both Google & Microsoft have services which monitor and will warn if you are visiting a malicious website.This feature does not detect all malicious websites, so again check with your IT department.
3. Manual Smart Attack
Smart attacks can come in many forms, and it can leave you second-guessing yourself.An excellent example of a smart attack we recently encountered was an email sent to an HR manager just before payroll was about to be run.

The email in question appeared to be from a senior director in the company instructing the HR manager if he could update his personal bank details for payroll.The email itself looked legitimate, and the only thing that stopped them instruction going through was the HR manager who asked the senior director to confirm.This attack was so smart that there’s no real way for software or systems to overcome it. As such, it’s essential that staff are aware of the threats that can come in many forms from email. For this reason alone it is imperative that all of your staff members go through some form of Security Awareness Training or SAT. At XpressteX we offer 30-Days trial for a Cybersecurity Awareness Training. You can get in touch by Clicking Here.
Decoding Manual Smart Attacks
The Anatomy of a Manual Smart Attack
Manual smart attacks, also known as targeted attacks or advanced persistent threats (APTs), are sophisticated and stealthy cyber-attacks that specifically target high-value individuals or organizations. Understanding the anatomy of these attacks can help you recognize the signs and devise effective defense strategies:
1. Reconnaissance: Attackers gather detailed information about their target, including their online presence, social connections, and potential vulnerabilities.
2. Initial compromise: This phase involves breaching the target's defenses, often through techniques like spear-phishing emails, watering hole attacks, or exploiting unpatched software vulnerabilities.
3. Lateral movement: Once inside the target's network, attackers maneuver through the environment, escalating privileges and gaining access to valuable resources or sensitive information.
4. Exfiltration: Attackers exfiltrate the stolen data or establish persistent access for future attacks, leveraging various techniques to evade detection and cover their tracks.
Strategies to Defend Against Manual Smart Attacks
Defending against manual smart attacks requires a multi-layered approach that combines technical measures with vigilant security practices. Here are some strategies to strengthen your defenses:
1. Conduct regular security assessments: Regularly assess your organization's security posture, identifying and addressing vulnerabilities promptly. This includes conducting penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and social engineering simulations.
2. Implement robust access controls: Limit user privileges and use role-based access control (RBAC) mechanisms to ensure employees have access only to the resources necessary for their roles. Monitor user activities and enforce strong password policies to prevent unauthorized access.
3. Invest in employee awareness and training: Educate your employees about the risks associated with manual smart attacks, emphasizing the importance of strong passwords, identifying phishing emails, and adhering to security best practices. Regular training sessions and simulated phishing exercises can significantly increase awareness.
4. Deploy advanced threat detection and response solutions: Utilize intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM) tools, and endpoint protection solutions to monitor network traffic, detect anomalies, and enable swift incident response.In conclusion, defending against spoofing attacks requires a proactive and comprehensive approach. By understanding the different types of spoofing techniques, learning how to detect and prevent email spoofing, identifying cloned websites, and decoding manual smart attacks, you can enhance your ability to protect yourself and your organization. Stay vigilant, keep your software up-to-date, educate yourself and your team, and implement appropriate security measures to reduce the risk of falling victim to these malicious attacks.



